Best Practices for Real-Time Sports Data Processing
Practical guide to building low-latency sports data pipelines covering ingestion, validation, caching, scaling, and real-time delivery.

Real-time sports data processing is about delivering live updates - like scores, stats, or sensor data - instantly to users. This is critical for fantasy sports, live betting, and fan engagement, where even a one-second delay can cause frustration or financial loss. However, managing this data comes with challenges like traffic spikes, data inconsistencies, and system bottlenecks.
To build an efficient real-time system, focus on these key steps:
- Data Ingestion: Use tools like Apache Kafka or AWS Kinesis to handle high-speed data streams.
- Storage: Combine in-memory solutions (e.g., Redis) for fast access with cloud storage (e.g., Amazon S3) for archiving.
- Scalability: Implement horizontal scaling and serverless architectures to handle traffic surges during major events.
- Data Validation: Standardize and validate data to ensure accuracy across different sources.
- Caching: Use multi-tiered caching for static data and instant invalidation for live updates.
- Latency Reduction: Optimize APIs and delivery methods (e.g., WebSockets) to achieve sub-100ms response times.
Platforms like StatPro simplify this process by offering low-latency APIs, real-time updates, and built-in data corrections for leagues like the NFL, NBA, and MLB. By following these practices, you can create a fast, reliable system that meets the demands of modern sports analytics.
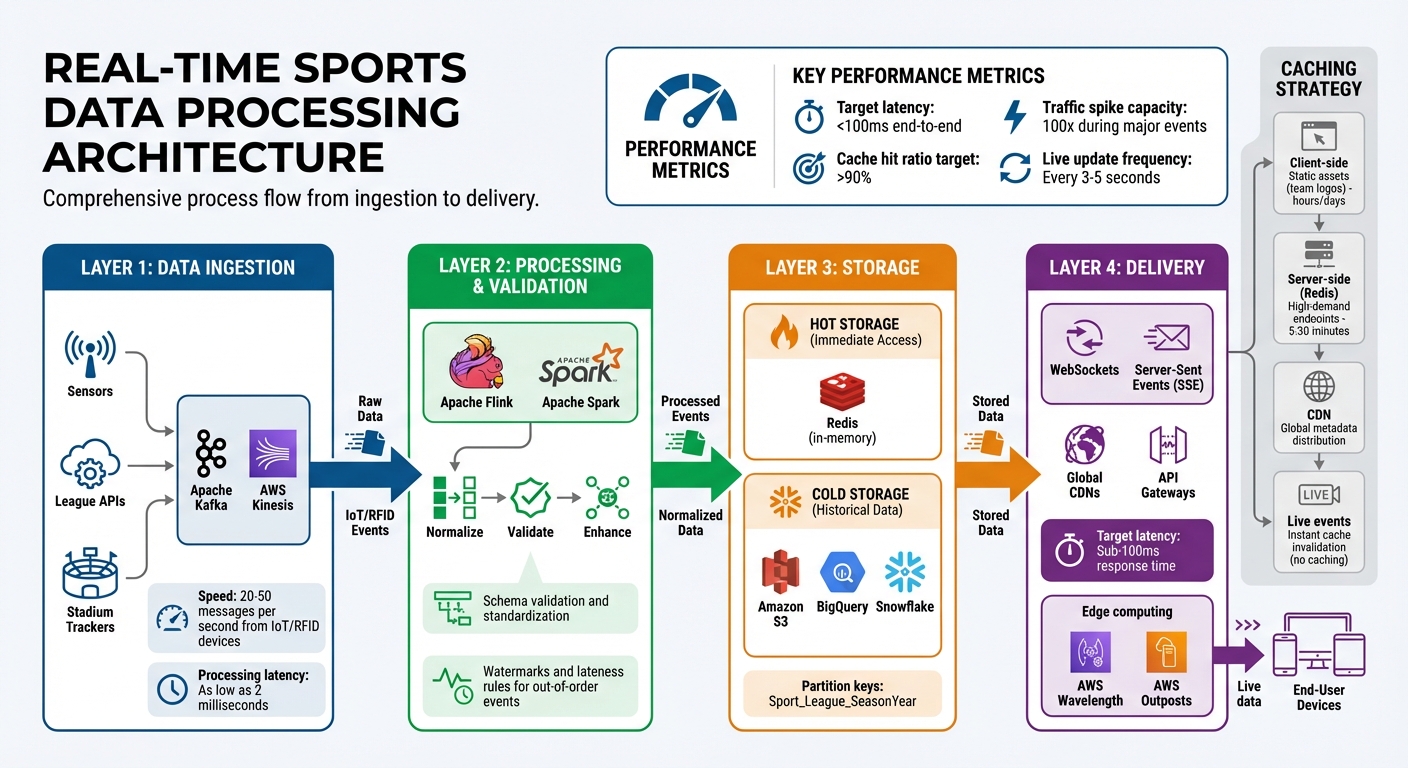
Real-Time Sports Data Processing Architecture: From Ingestion to Delivery
Building a Scalable Data Infrastructure
Architecture for Real-Time Data Systems
Real-time systems rely on a well-coordinated mix of ingestion, processing, storage, and delivery layers. The ingestion layer captures high-speed data streams using tools like Apache Kafka or Kinesis, pulling in data from sources such as sensors, league APIs, and stadium trackers. Once ingested, frameworks like Flink or Spark step in to normalize, validate, and enhance the incoming data in real time.
Storage is split into two categories: "hot" storage, which uses in-memory solutions like Redis for immediate access, and "cold" storage, which archives historical data in platforms such as Amazon S3, BigQuery, or Snowflake. On the delivery side, updates are pushed to users through WebSockets or Server-Sent Events (SSE), with global CDNs and API gateways helping to reduce latency.
At the heart of this setup are event-driven microservices. These small, independent services communicate through message brokers, making it easier to scale individual components as needed. For critical applications like live betting or player health monitoring, edge computing solutions, such as AWS Wavelength or AWS Outposts, bring data nodes closer to the source to cut down on latency even further.
Once this architecture is in place, the next step is creating efficient data pipelines to ensure smooth and fast data movement.
Designing Data Pipelines for Sports Analytics
In live sports analytics, uninterrupted data flow is non-negotiable. Pipelines need to adopt a "push" mechanism instead of a "pull" approach to ensure data moves through the system instantly. A unified schema is crucial here - it standardizes raw data from various providers into a single format. This abstraction allows you to switch data sources without having to redesign your user interface.
"The world of sports data will definitely call for mapping one value to another." – Akash Barve, Software Engineer II, Fanatics
Partitioning in NoSQL databases is another critical factor. Logical partition keys, such as Sport_League_SeasonYear, help avoid costly cross-partition queries, which can bog down performance during high-traffic events. Consider this: IoT devices or RFID chips embedded in player gear can generate anywhere from 20 to 50 messages per second. Your pipeline must be robust enough to manage these continuous, high-speed streams without bottlenecks.
Strong pipelines are only as good as the infrastructure supporting them, especially when dealing with massive traffic spikes.
System Reliability and Scalability
Handling traffic surges requires a focus on horizontal scaling - adding more servers as needed - rather than depending solely on vertical scaling. Using CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation) ensures that heavy data ingestion processes don’t interfere with user-facing queries. If your primary data feed fails, automated failover mechanisms can seamlessly switch to a backup provider, keeping your system reliable.
For distributed Azure setups, disabling Application Request Routing (ARR) affinity ensures traffic is evenly spread across all instances. Serverless solutions like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions are particularly useful for managing data transformations, as they scale automatically with incoming demand and keep costs in check. To further boost performance, Redis caching can reduce network calls for frequently accessed data, such as live scores.
Finally, regular load testing is essential. Simulating traffic spikes at least 10 times higher than your previous peak can uncover potential bottlenecks before they disrupt your system.
Best Practices for Real-Time Data Processing
Stream Management and Event Processing
When working with real-time data, designing an infrastructure that can handle events instantly is key. A stream-to-stream approach processes live events with minimal delay - sometimes as low as 2 milliseconds when using tools like Apache Kafka. For context, IoT devices and RFID chips embedded in sports equipment can generate between 20 and 50 messages per second.
However, live sports data often faces challenges like out-of-order events caused by network lags or clock mismatches. For instance, a play-by-play update might arrive after the next event has already been recorded. To address this, systems use watermarks and lateness rules, which establish a waiting period for late-arriving data. This ensures that time windows are finalized correctly and that joins and aggregations remain accurate.
"Real time is not 'we use streaming.' Streaming is a technique; real time is an outcome."
- CelerData
Monitoring tail latency is another crucial step. Instead of relying on averages, focusing on P95 and P99 latency metrics can uncover performance spikes, especially during high-pressure moments like playoff games. For example, Netflix's real-time observability platform, built with Kafka and Druid, processes over 2 million events per second and queries across 1.5 trillion rows - all with sub-second response times.
With events being processed so quickly, rigorous data validation becomes non-negotiable.
Data Validation and Standardization
For data to be useful, it must be accurate, consistent, complete, and dependable. Automated checks can catch errors immediately, preventing issues like negative travel distances or unrealistic scoring changes from skewing analytics.
"Data validation ensures that the data collected, analyzed, and used to make critical decisions is accurate, consistent, and useful."
- The Athlete's Edge
Each sport comes with its own unique metrics, requiring tailored validation processes. For example, the NFL might focus on wearable fatigue data, while the NBA emphasizes shot analytics, and MLB tracks highly detailed statistics. To ensure consistency, using XML schemas and Open API Specifications (OAS) helps standardize data structures, making it clear which data points applications should expect.
Cross-validation adds another layer of accuracy. For instance, wearable GPS data can be compared against video analysis to confirm physical performance metrics. Regular calibration of devices like GPS trackers and heart rate monitors ensures precise raw data. High-performance live data systems can even deliver updates from the venue to the end-user in under a second.
Validation processes also play a critical role in managing unexpected anomalies and edge cases.
Handling Edge Cases and Data Corrections
Real-time systems must perform consistently, even under unpredictable conditions. One way to ensure this is by validating schemas as soon as data is ingested and isolating "poison messages" to prevent downstream crashes. Storing raw data as individual blobs allows for comparisons between new and previous versions, so only meaningful changes trigger further processing. This avoids wasting resources on duplicate information.
Fuzzy string matching can help identify duplicate records caused by minor inconsistencies, such as variations in capitalization or spelling of athlete names (e.g., "Alameda Ta'amu" vs. "Alameda Ta'Amu"). It's also wise to include default fallback values for data mapping - like player positions, season types, or venue IDs - to keep the pipeline running smoothly even when unexpected values appear. If mapping errors occur, triggering immediate alerts via Slack or email allows the team to intervene without halting the entire process.
Building idempotent data sinks ensures that duplicate entries are avoided during replays. For large-scale data corrections or refreshes, using delayed queues with visibility timeouts prevents the system from being overwhelmed by thousands of updates at once. Finally, testing edge cases with tools like Postman or through simulated game scenarios helps verify that your system can handle unexpected situations, such as 302 redirects, 304 Not Modified responses, or sudden feed outages.
Improving Performance and User Experience
Caching Strategies for Real-Time Systems
A smart caching strategy can turn sluggish, multi-second responses into lightning-fast delivery. For sports data, multi-tiered caching is particularly effective. Start with client-side caching (like browsers or mobile apps) for static assets such as team logos. Add server-side in-memory stores like Redis for high-demand endpoints, and use CDNs to distribute global metadata efficiently.
The trick lies in aligning cache durations with how often the data changes. For instance, historical game results can be cached for hours or even days, while league standings might need updates every 5–30 minutes. However, for live events like goals or turnovers, caching is a no-go. Instead, implement instant cache invalidation for these updates to keep things real-time.
"A well-placed cache stores frequently requested data closer to the user, allowing a multi-second API response to be delivered almost instantly." - David Jaja, Sportmonks
Real-world examples show how impactful caching can be. Spotify slashed median latency from 120ms to just 17ms by fine-tuning hot key retention per microservice. Pinterest cut database IOPS by 70% by adopting a write-behind architecture for non-critical logs. For sports data, you can use Redis EXPIRE commands to set explicit TTLs - like 2 seconds for live game updates and 120 seconds for post-game stats. Keep an eye on your cache hit ratios; aim for at least 90% on read-heavy endpoints. Falling short often points to inadequate memory or inefficient eviction policies.
| Caching Method | Best Fit | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cache-Aside | Read-heavy, infrequent writes | Simple, resource-efficient | Risk of stale reads, manual eviction required |
| Write-Through | When strict consistency is needed | Guarantees freshness, minimizes stale data | Slower write performance |
| Write-Behind | High-write, performance-critical scenarios | Maximizes throughput, reduces DB strain | Risk of data loss if cache fails |
| Read-Through | Seamless integration | No need for manual miss handling | Limited control, often vendor-specific |
Once caching is optimized, the next focus is on API strategies to further enhance real-time data delivery.
API Usage for Real-Time Data
Using RESTful APIs combined with push feeds is a great way to minimize latency. One effective method is intelligent polling, which adjusts the frequency of requests based on the game's status. For example, poll "pending" games (those in progress) while skipping completed or upcoming ones to save resources.
Another smart move is fetching only updated data. Delta or Change Log APIs can return just the points that have changed within a given timeframe - say, the last minute - instead of pulling entire datasets. This approach significantly cuts down on bandwidth usage and processing demands. Make sure your polling intervals align with the live TTL settings to avoid unnecessary calls and potential rate-limiting.
To ensure flexibility, normalize data from different sources into a unified format. This way, you can swap data providers without having to redo your user interface. Also, optimize your API configurations to balance the load effectively. For accuracy, schedule a daily refresh of box score data from the past 48–72 hours to account for any mid-week stat corrections.
With APIs optimized, the focus shifts to presenting live data in an engaging and timely manner for users.
Real-Time Data Presentation and User Feedback
After fine-tuning caching and APIs, the final step is delivering live data to users with minimal delay. The goal? Sub-100ms latency from the moment an event happens to when it appears on the screen. During major events like the Super Bowl or FIFA World Cup, traffic can spike by 100x within minutes, so speed and reliability are critical.
"Fans don't see Kafka clusters or Redis caches; they just see whether the goal notification hits their screen before it appears on TV." - Data Sports Group
Adding a "last updated" timestamp is a simple but effective way to reassure users about data freshness. Also, transform cryptic API codes (like "QB") into user-friendly terms ("Quarterback") to improve clarity and build trust.
"For live apps, it's better to show 'almost accurate' data quickly, then reconcile in the background. Users value speed over perfection." - Data Sports Group
To maintain a seamless experience, set up alerts - via Slack or email - for unmapped data, such as a new venue or player. This ensures you can address issues before they affect users. Additionally, account for sport-specific quirks, like triple-header games in MLB or overtime losses in the NHL, to prevent errors in unusual scenarios.
Using StatPro for Real-Time Sports Analytics
StatPro Features for Real-Time Sports Data
StatPro provides comprehensive coverage for the NFL, NBA, and MLB, offering real-time play-by-play data, scores, and stats through its APIs. With low-latency push feeds and RESTful APIs, the platform delivers live updates alongside access to historical data.
To maintain accuracy, StatPro automatically manages post-game stat corrections. For example, official NFL statistics may be updated as late as the Friday following a game. The system also uses Delta data processing, which sends only updated player stats, helping to reduce both bandwidth usage and processing demands.
These features make it easy to integrate StatPro into your workflow while ensuring reliable, up-to-date data.
Integrating StatPro into Your Workflow
Getting started with StatPro is a simple process. Integration happens in three key steps:
- Step 1: Begin with foundational data, such as team details, standings, and league structures. This data syncs daily during off-hours.
- Step 2: Move on to pre-game data like projections and lineups, which refresh every 10 minutes in the 4–6 hours leading up to a game.
- Step 3: Use real-time game updates with Delta API calls, which can refresh as often as every 5 seconds for live applications.
For efficient operations, set up a server-side task to monitor "Pending Games." This triggers high-frequency data pulls when needed. If you're working with MLB data, pay close attention to the "BattingOrderConfirmed" field, which typically updates 3–4 hours before a game. This ensures a smooth transition from projected to official lineups. StatPro also integrates with third-party platforms like Sleeper, providing personalized fantasy insights powered by real-time data.
Benefits of Using StatPro for Sports Data Processing
StatPro simplifies sports data management by centralizing information and streamlining API usage. Its structured data paths - from league hierarchies to team and player profiles - reduce unnecessary API calls and ensure data consistency. This eliminates the need to normalize data from multiple providers, saving time and resources.
The platform's league-specific architecture offers deep insights, including full play-by-play coverage and real-time stats. Additional features, like modules for matchup comparisons, conference standings, and detailed player stats (points, rebounds, assists, etc.) for the NBA, enhance analytical capabilities. For fantasy league managers or developers building sports applications, StatPro delivers reliable, real-time data without the hassle of maintaining complex systems.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Summary of Best Practices
Building a real-time sports data system demands efficiency, speed, and accuracy. To manage sudden traffic surges - like those seen during major events, where traffic can spike by 100x - use streaming ingestion tools such as Apache Kafka or AWS Kinesis, paired with a canonical data model. This combination ensures smooth handling of spikes and allows for seamless provider switching without disrupting the system. For better performance, implement in-memory stores like Redis, which help maintain high cache hit rates and significantly reduce database load.
Another critical step is mapping global unique identifiers from vendors to your internal IDs. This prevents duplicate records and ensures data integrity. Automating anomaly alerts, sent via tools like Slack or email, allows you to quickly address issues such as unmapped venues or athletes. These strategies form the backbone of a reliable system, paving the way for successful implementation.
For an all-in-one solution, StatPro offers low-latency APIs, Delta data processing, and automatic stat corrections for leagues like the NFL, NBA, and MLB. Its structured data paths minimize unnecessary API calls, while features like real-time play-by-play updates and access to historical data showcase how these principles can be applied effectively.
Next Steps for Implementation
To bring your real-time sports data system to life, focus on these actionable steps:
- Define your data model: Map external provider IDs to your internal system to handle edge cases, such as MLB triple headers or NHL overtime losses.
- Set sync intervals: For example, update live scores every 3–5 seconds, odds every 5–10 seconds, and rosters hourly.
- Leverage serverless architectures: These scale automatically during high-traffic moments, and edge computing nodes can be positioned closer to users for faster delivery.
- Integrate StatPro: Sync foundational data daily and refresh pre-game projections every 10 minutes for up-to-date insights.
- Test extensively: Run game simulations before going live, and monitor system performance using tools like Application Insights or PagerDuty.
An AI Understanding of Football: Automated, Real-Time Data Capture | SportsInnovation 2024
FAQs
How can real-time sports data systems manage sudden traffic surges effectively?
To manage sudden spikes in traffic, real-time sports data systems need flexible architectures that can handle fluctuating demands. Cloud-based solutions with elastic infrastructure are a great option, as they can automatically adjust resources up or down during peak periods. This ensures smooth performance, reduces the risk of downtime, and spreads traffic across multiple servers and regions to keep latency low - even during major events.
Another key component is using streaming data pipelines. These pipelines allow for continuous processing of high-speed data, avoiding bottlenecks and ensuring updates happen in real time. Techniques such as load balancing, caching, and event-driven triggers play a crucial role in boosting system reliability. By combining these methods, platforms can maintain a seamless user experience, even when traffic surges unexpectedly during live sports events.
What are the best ways to minimize delays in real-time sports data processing?
Minimizing delays in processing real-time sports data hinges on smart system architecture and the right tech stack. The key is to create a scalable, low-latency data pipeline capable of quickly handling data from ingestion to delivery. Leveraging high-performance tools like Apache Druid or ClickHouse can make data querying and analytics faster and more efficient.
Cloud platforms like AWS and Microsoft Azure can also play a big role in reducing latency. Features such as edge computing and regional data centers allow data to be processed closer to the end user, cutting down transmission times significantly. Pair this with efficient data ingestion methods - whether through APIs or IoT devices - to ensure a smooth and uninterrupted data flow.
By integrating these approaches, you can provide near-instant updates for live scores, player stats, and fan-focused applications.
Why is data validation important for real-time sports analytics?
Data validation plays a crucial role in maintaining the accuracy and dependability of real-time sports analytics. By ensuring that incoming data is complete, consistent, and error-free, it helps avoid inaccuracies that could mislead teams, broadcasters, or fans. The process involves critical checks like confirming data freshness, verifying source completeness, and ensuring schema consistency.
In the fast-paced world of live sports, where information like player stats, game scores, and team standings is updated constantly, validation becomes even more important. It helps identify and fix issues that can arise from large data volumes or transmission errors. This ensures updates remain accurate and timely, safeguarding the quality of analytics. Whether it’s for live commentary, performance analysis, or engaging fans, dependable data is essential for making informed decisions and enhancing the overall experience.